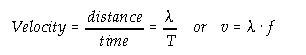Mechanical Waves

'
 Traveling Waves
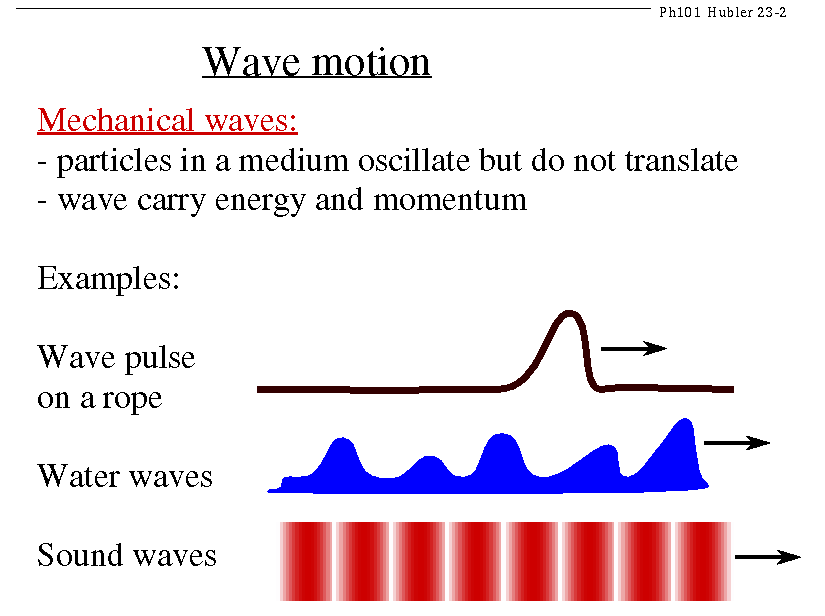
Traveling WavesIn general, a wave is a propagating disturbance of some equilibrium, quiescent state. The thing that is being disturbed is usually a continuous medium (such as a fluid), but it can also be something that is not itself a material, such as the temperature in a heat wave. Further, the medium does not itself have to move very far - what is important is that the disturbance should move along. Think of a wave in a field of grain: each stalk moves only a little bit, but the wave moves across the whole field. One of the easiest types of wave to demonstrate is a wave on a rope. Move one end of a stretched rope up and down, and a `hump' will travel along the rope, away from your hand.
PBS: Traveling WavesTypes of Waves
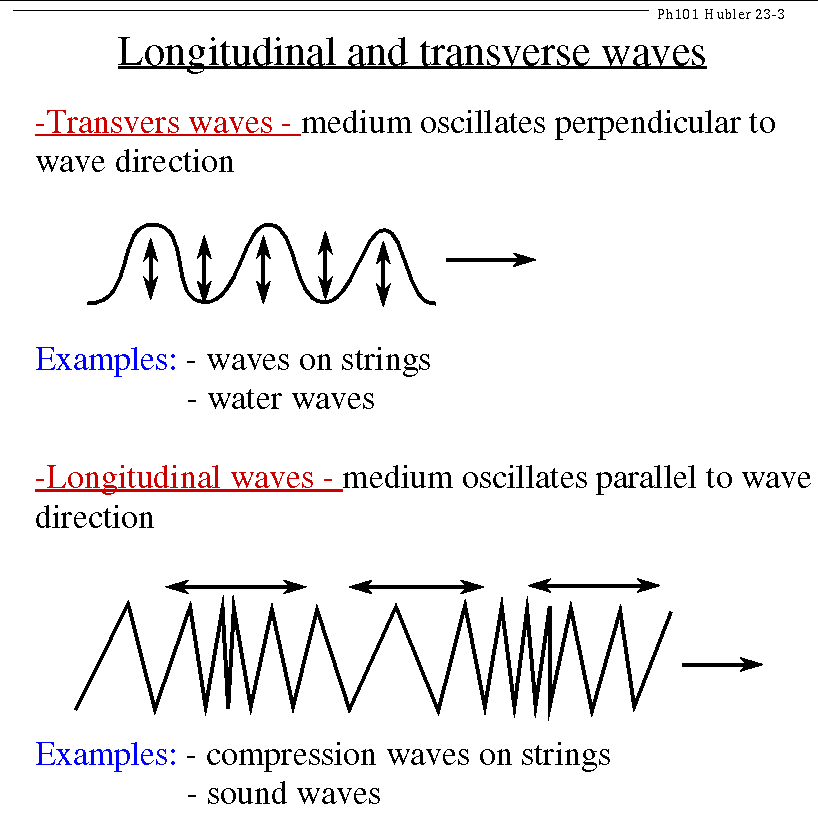
Transverse: side to side oscillation
Longitudinal: oscillation in direction of travel
v = wave speed
More sophisticated: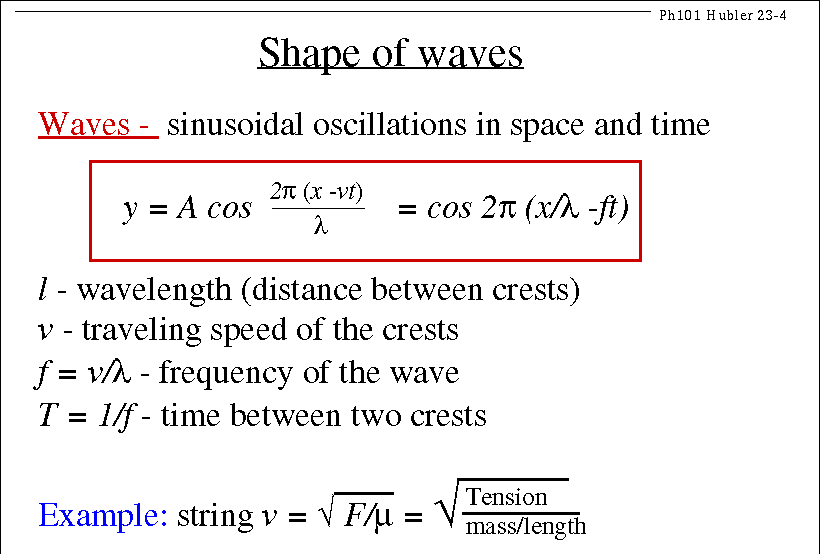
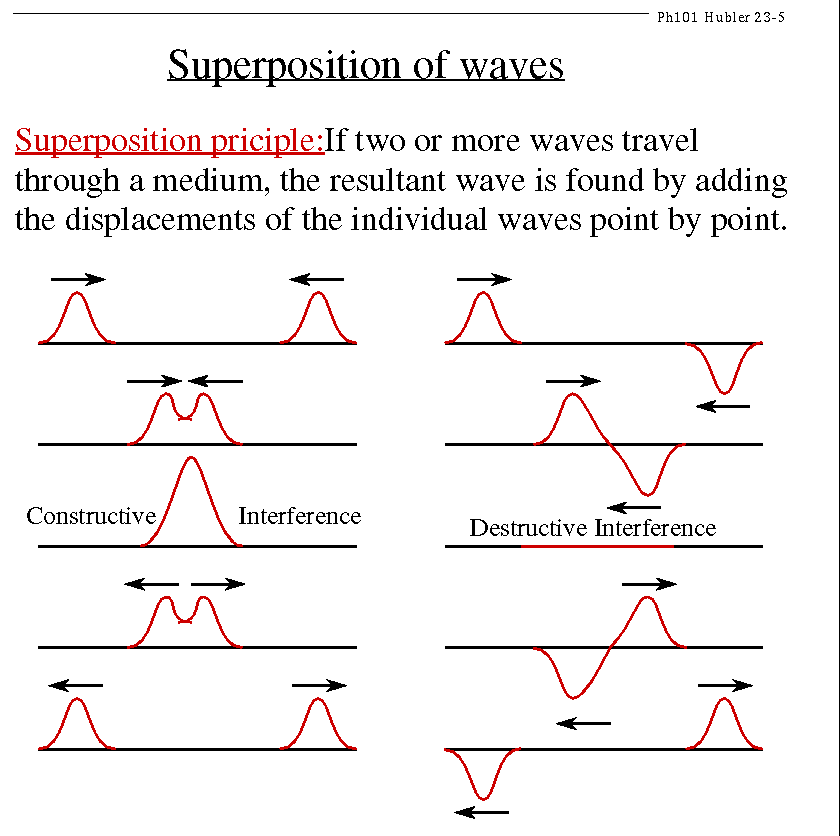
"Adding"
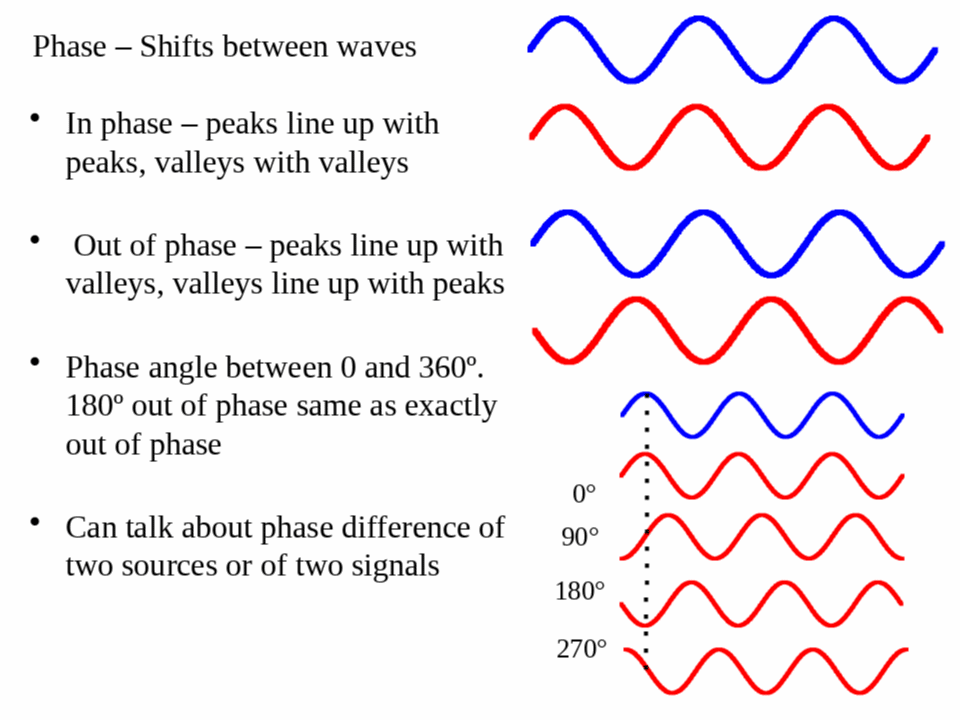
In-phase ... Out-of-phase
Result:
bigger amplitude or zeroamplitude
Constructive interference or Destructive interference
Animation: Superposition of WavesSuperposition of Waves
When waves encounter:
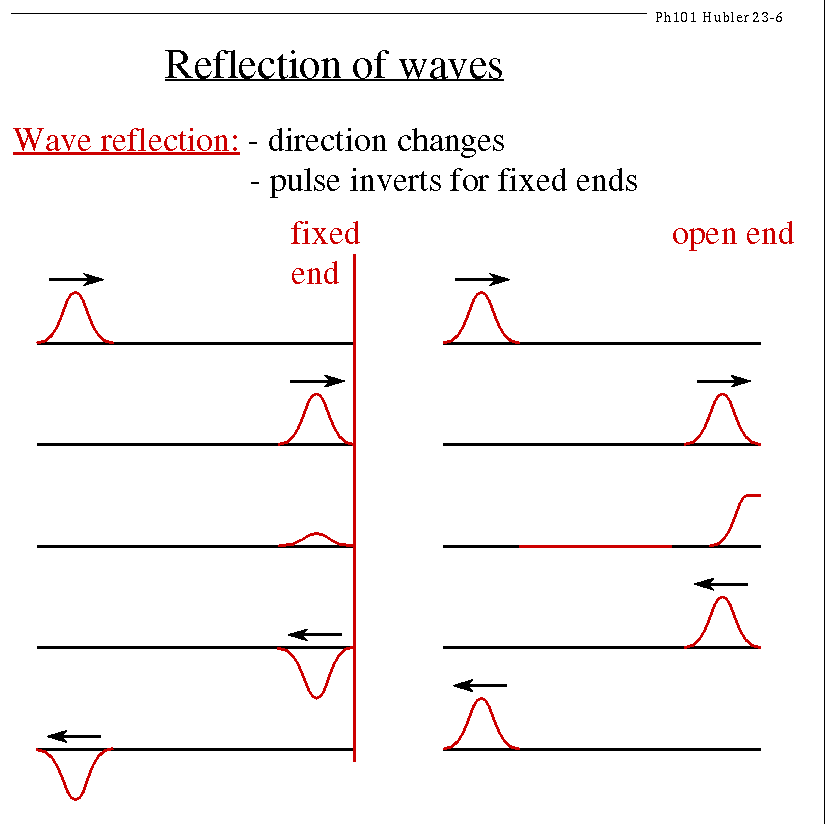
a harder barrier, the energy is reflected (i.e., they "bounce") a softer barrier, the energy is
absorbed.
reflected waves can be in-phase or out-of-phase.
Stone in water : Circular pattern Plane Waves -----> WavesSpherical Wave front Surface of sphere: 4r2 pi
Wave carries energy ( intensity) For spherical waves, intensity decreases 1/r2
Wave front gets disturbed by small opening. wave length of Sound: 0.3 - 0.5 m wave length of Light: 10-7 m Diffraction occurs only when the wavelength is about the same size as opening. "You cannot see around the corner."
 Reflection Reflection
 Diffraction Diffraction
 Refraction Refraction
|

Ch. Elster
Aug 26 14:27:03 EDT 2019