
Color I



 Rayleigh Scattering
Rayleigh Scattering
|
Rayleigh Scattering occurs if light encounters objects which
are much smaller than the wavelength of this incident light.
In addition, these objects must have their important resonances at
frequencies greater than those of light.
 Rule for Rayleigh Scattering Rule for Rayleigh Scattering
The consequence of this scattering process is
Consider this sketch of sun and earth:
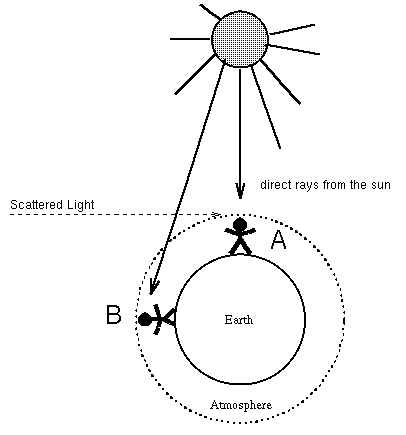
After volcano eruptions sunrises and sunsets can be very colorful. The reason is that there is a lot of dust in the air. Why are clouds white? Water droplets are much larger ( about 50 times) than the wavelength of light. When there are many surfaces to present to reflect light, almost all light is scattered. ==>
Of course: very dense clouds DO NOT transmit
light.
Experiment Light scattering from milk Light scattering from milk
Try it! Blue skies.Experiment from the St. Louis Science Center

|
Ch. Elster