- Scientific Method
- Can you describe the different elements constituting the
scientific method?
- What is meant by observation and identifying patterns? What is
important for the process?
- What is a hypothesis and a theorem?
- Units
- An answer of 200 is not sufficient (200 meters or 200 kilometers?)
- What are the fundamental units in the SI system?
- Do you understand scientific notation?
- Defining equations
- velocity = (change in distance)/time [units = m/s]
- acceleration = (change in velocity)/time [units = m/s
 ] ]
- force = mass
 acceleration [units = kg-m/s2] acceleration [units = kg-m/s2]
- work = force
 distance [units = N-m] distance [units = N-m]
- pressure = force/area [units = N/m2]
- gravity is an example of acceleration [g = 9.8 m/s2]
- weight is an example of a force [W = mass
 g] g]
- Newton's Laws
- 1
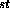 Law: defines inertia Law: defines inertia
- 2
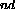 Law: F = ma Law: F = ma
- 3
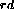 Law: for every force, there is a reaction force Law: for every force, there is a reaction force
- Energy
- Work is an example of energy
- Energy can be stored (potential energy)
- Motion is a form of energy (kinetic energy)
- Temperature
- Temperature is a measure of the internal energy of an object
- Can you convert from Fahrenheit to Celsius?
- Can you convert from Celsius to Kelvin?
- T = 0 K (zero Kelvins) means zero internal energy
- There are no negative temperatures as measured in Kelvins
|




