|
- Oscillations
- What force is present for an oscillating system?
- Define T = the time `period' (time for one cycle)
- Define f = 1/T = the `frequency' (number of cycles per second)
- The energy of the system oscillates between stored energy and energy
of motion
- What do in-phase and out-of-phase mean? Can you draw a picture?
- Examples of oscillating systems
- a mass attached to a spring
- a pendulum
- a ball in a bowl
- an atom in a crystal (this has very small oscillations)
- Traveling waves
- Some materials have elastic properties (even glass!)
- The energy in a traveling wave transfer from one atom to the next
- What are transverse waves?
- What are longitudinal waves?
- Can you give examples of longitudinal or transverse waves?
- Define
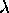 = wavelength. Can you draw this? = wavelength. Can you draw this?
- The velocity of a wave is v =
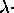 f, where f = frequency f, where f = frequency
- Standing waves
- Traveling waves can be reflected by a hard surface
- What is the condition for standing waves to occur?
- A stretched string of length L has standing waves when 2L = n
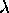 ,
where n can take on the values of 1 or 2 or 3 or . . . ,
where n can take on the values of 1 or 2 or 3 or . . .
- Resonance
- What is meant by the `natural frequency' of an oscillating system?
- Pulsing the system at its natural frequency creates a 'resonance'
- Large vibrations results when resonance occurs. Can you draw this?
- What are examples of designed (useful) resonance?
- What is an example of a 2-dimensional resonance?
|




