|
- Sound terms
- What are common usage terms for `amplitude', `frequency', and `waveform'?
- How is a wave attenuated?
- What is the velocity of sound waves in room-temperature air?
- Sound can be reflected (echo).
- Sound waves can be refracted due to different air temperatures.
- Mechanism of sound travel
- Sound waves travel due to the collision of molecules in the air
- Can sound travel through a vacuum?
- Can sound travel through water? through solids?
- Standing Waves in Tubes
- An open-open pipe has standing waves of 2L = n
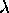 ,
where n = 1, 2, 3, . . . ,
where n = 1, 2, 3, . . .
- An open-closed pipe has standing waves of 4L = m
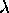 , ,
where m = 1, 3, 5, . . .
- Sound Intensity
- Define power = energy/time [units = Watts]
- Define intensity = power/area [units = Watts/m2]
- The threshold of hearing is I0 = 10-12
Watts/m2.
- Define the sound level B = 10 log (I/I0) [units = dB]
- Loudness is a subjective measure and depends on the
individuals perception and physical condition of the ear.
- Doppler effect
- What causes the Doppler effect? Can you draw a picture?
- How does the frequency (pitch) change for a known velocity?
- What causes sonic booms?
- Beats
- We hear different vibration frequencies as different pitches
- Two vibrations in-phase sound twice as loud; two vibrations
out-of-phase cancel (sound very faint)
- When two notes of slightly different frequency as
rounded at the same time, a 'vibrato' is heard, also known as 'beats'
Can you explain the beats pattern in terms of in-phase
and out-of-phase vibrations?
- The beats pattern can be used to get two musical instruments in tune
- Tone quality
- The tone quality, also known as the timbre, is determined by the
number of harmonics heard, and the loudness of each harmonics.
- A sound with more harmonics is said to have a 'richer' timbre.
- A tuning fork has a nearly pure tone, it has very few harmonics.
- Many musical instruments, such as the trumpet, have 30 or more
harmonics.
- Attack and decay of a note determine its sound.
- The formant region of an instrument is the frequency region which
is emphasized relative to other harmonics and determines the unique
sound of an instrument.
- A vibrato is produced by periodic changes in the pitch of a
musical tone.
- A tremolo is produced by periodic changes in the amplitude of a
musical tone.
- A chorus effect occurs if many instruments play the same part in
unison. The sound quality is quite different from the individual
instruments
due to superposition of many similar tones with slightly different
frequencies and tone qualities.
|




