|
- Light shows wave properties
- Diffraction: waves spread out after they pass through an aperture
(small opening)
- Refraction: waves will `bend' when going through certain materials
- What is light?
- An electric `field' surrounds all charged objects
- An oscillating charge will produce as oscillating electro-magnetic field
The oscillating electro-magnetic field propagates as transverse
wave.
- Electro-magnetic waves of a certain frequency (wavelength) are
perceived as `light'.
- We perceive different frequencies of light as different 'colors'
- All hot objects emit light.
- A black-body is a body that absorbs all radiation that falls on it.
- When a black body is heated, it starts to glow and emits a
characteristic black-body spectrum.
- More energy is emitted from hot objects than from cool ones. The
peak emission occurs at higher frequencies for hot objects, at lower
frequencies for cooler objects.
- An electron, such as those in the atoms in your eye, will be
pulled along with the oscillating electric field. This is how we
`see' light
- The electrons in an atom or molecule can absorb or emit photons
(light quanta of a certain energy) and thus produce a discrete
spectrum.
- Emission spectrum: Atoms or molecules emit photons (light quanta)
of a certain discrete energy when the electrons jump from a higher level
to a lower level. These photons have an energy characteristic for the
atom or molecules, thus show distinct colors in the visible spectrum.
- Absorption spectrum: Atoms or molecules absorb photons of a
certain energy, thus there are black lines (missing frequencies) in the
light spectrum.
- Light wavelengths
- The wavelength is related to the frequency be
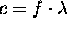
- The speed of light in the vacuum is c = 3 * 10 8
m/s .
- Very long wavelengths of light are called radio waves
- Long wavelengths of light are called infrared.
- Visible light has wavelengths of 400 to 700 nanometers (a nanometer
is one billionth of a meter, or 10-9 meter).
- Short wavelengths of light are called ultraviolet
- Light Sources
- Incandescent light: produce light through being heated, e.g.
light bulbs, candles.
- Fluorescence: The process of absorbing ultraviolet light and
emitting visible light. Excited atoms in fluorescent materials drop to
their normal level in about 10-8 s.
- Phosphorescent materials continue to glow long after the
illumination has been removed. The atoms remain in an excited metastable
state for periods ranging from a few seconds to several hours.
- Triboluminescence: The process of producing light by mechanical
forces exerted on an object (e.g. crushing a wintergreen candy).
- Photometry
- Intensity is power per unit area and is measured in cd
[candles].
- Luminance: intensity per unit area [candles/m2].
- The intensity falls of inversely proportional to the square of the
distance from the light source.
|




