Chapter 5e -
Function set simple - a Simple
simulation of a specific Stirling engine configuration
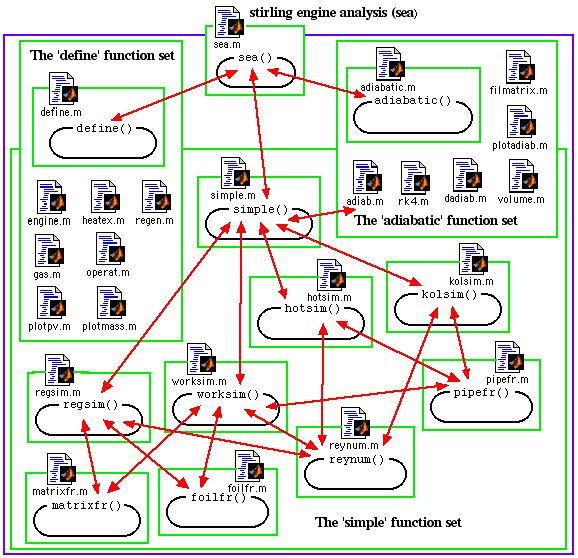
From the flow
diagram below we see that the main program sea
(stirling engine
analysis) first defines the system to be simulated in terms of the
set of global variables set up by the define
set of functions, as
described previously. It then invokes either the function adiabatic
which does an Ideal
Adiabatic simulation, or the function simple
to do a Simple
simulation to evaluate the heat transfer and pressure drop loss
effects. Function set 'simple' includes nine functions, all contained
in separate m-files as shown. The four main functions are hotsim
and kolsim
to respectively
evaluate the heater and cooler gas temperatures, regsim
to evaluate the
regenerator effectiveness and resulting enthalpy loss, and worksim
to evaluate the
pumping loss. The heat-transfer/flow-friction
function set
includes function reynum
to evaluate the
instantaneous Reynolds Number, and the three functions pipefr,
foilfr
and matrixfr
to determine the
various flow friction and heat transfer coefficients.
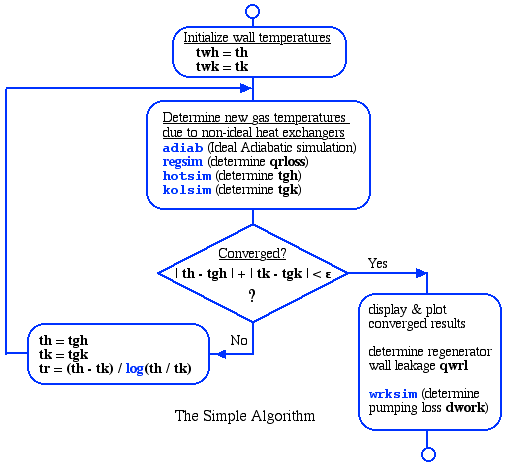
The
dynamics of the solution algorithm lies in function simple,
as shown in the
following flow diagram. Thus the function set define
specifies the
operating conditions, including the temperature bounds th
and tk.
Since the temperature bounds of the working gas affect both the power
output and efficiency, the simple routine invokes adiab,
regsim,
hotsim,
and kolsim
in a loop until
convergence of the gas temperatures is attained.
The nine
functions of the set simple
are included in the
following m-files (refer to the flow diagram above): [simple.m,
hotsim.m,
kolsim.m,
regsim.m,
reynum.m
,
worksim.m,
pipefr.m,
foilfr.m
and matrixfr.m].
As before, these can be directly copied from this website and used in
a system which has MATLAB installed.
Notice
that there are a limited number of heat exchanger configurations
specified. It is intended that the user will modify and augment this
system as required for specific systems, and as more updated heat
transfer correlation data becomes available.
______________________________________________________________________________________

Stirling Cycle Machine Analysis by Israel
Urieli is licensed under a Creative
Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 United States
License

