Aerial Photographs and Remote SensingAerial PhotographsFor years, geographers have used aerial photographs to study the Earth’s surface. In many ways air photographs are better than maps. They provide us with a real world view of the earth’s surface, unlike a map which is a representation of the real world. Aerial photographs can be used to make the same measurements that we make on a map, as they too are a scaled image of the surface.
Figure 1.23 shows the rugged terrain one finds in the Front Range of the Colorado Rocky Mountains. North is at the top of the photograph. Alpine glaciers are found in favorable sites for snow and ice accumulation. Few of these glaciers are very active under present day conditions though. The glacier is easily identified by its white color. Surrounding the glacier on its western, southern, and eastern sides are the walls of a cirque in which it sits. A cirque is a bowl-shaped landscape feature common to mountainous regions which have been glaciated. The glacier formed in the area to the bottom of the picture and extended itself towards the north. The dark triangular - shaped feature to the north of the glacier is Triangle Lake. Remote Sensing and Satellite ImageryTo get a much larger view of the earth’s surface features, geographers have turned to using remotely sensed data from satellites. Satellite sensors scan the surface and break it down into picture elements or pixels like those displayed on your computer monitor. Each pixel is identified by coordinates known as lines (horizontal rows), and samples (vertical columns). As the satellite scans the ground, it transmits this information to earth-based receivers, the same way a television station broadcasts a signal to your television. The digital data received is processed in a variety of ways: simulated natural color, "false" color, signal filtering, enhanced contrast, etc.
Video: Watch "Remote Sensing: Observing the Earth
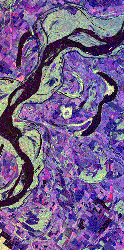
Figure 1.21 shows a portion of the Mississippi River that lies north of Vicksburg along the Arkansas-Louisiana-Mississippi state borders. The image was created from data obtained by Spaceborne Imaging Radar – C/X-band Synthetic Aperture imaging system aboard the space shuttle Endeavor. These images help scientists assess flooding potentials and land management along the river. Much of the area in purple is agricultural land. Areas occupied by water appear in black while the bright green areas are forested. The long narrow lakes bordering the river are called oxbow lakes and are created when the river changes course, abandoning the old channel for a new one. NASA has a detailed discussion (optional reading) about imaging radar online. Read how remote sensing is used to evaluate drought, desertification and the effect of war on Mozambique. |