Floods and Flooding
 A
flood
occurs when a stream channel can no
longer contain the water moving through it. Floods usually are local,
short-lived events, others can be catastrophic, happening with little
or no
warning. Floods are most often caused by prolonged rainfall that
saturates the
ground causing surface runoff into nearby streams increasing their
discharge.
Flooding occurs when the water spills out of the channel and on to the
adjacent
terrain. Though viewed as a "natural hazard" to humans, flooding is a
natural,
rejuvenating process.
A
flood
occurs when a stream channel can no
longer contain the water moving through it. Floods usually are local,
short-lived events, others can be catastrophic, happening with little
or no
warning. Floods are most often caused by prolonged rainfall that
saturates the
ground causing surface runoff into nearby streams increasing their
discharge.
Flooding occurs when the water spills out of the channel and on to the
adjacent
terrain. Though viewed as a "natural hazard" to humans, flooding is a
natural,
rejuvenating process.
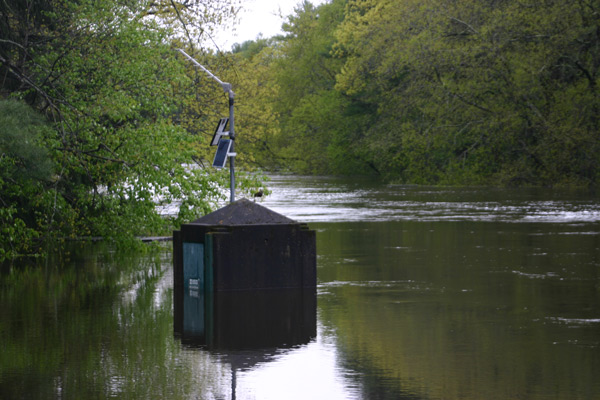
Figure 18.19 Flooded USGS gage, Lamprey River
near Newmarket, NH.
Courtesy USGS
(Source
)
Causes and Conditions
Generally speaking there are two types of floods, 1) where water slowly rises and spills over the banks of a stream or river and 2) flash floods. Floods can occur at anytime of year, but particular seasonal weather patterns are more conducive to the creation of floods than others in different geographic regions. In the United States, cyclonic storms roaring off the ocean and into the Pacific coast states during the winter and early spring can cause flooding. In the southwest, summer and fall thunderstorms release torrents of water that rush down dry stream beds or arroyos as flash floods. Flooding can occur in the north central states during the winter as rain fall or snow melt runs off the frozen ground surface, or ice jams rivers causing them to flood. Flooding in the mid portion of the United States tends to occur in spring and summer as polar front cyclones march across the North American continent. Hurricanes and large convective complexes create flooding in the late summer and fall along the Gulf coast of the United States.
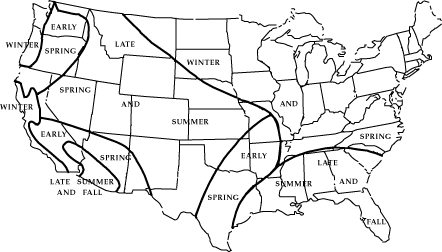
Figure 18.20 Flood Season in the United States Courtesy USGS (Source )
In tropical regions like Bangla Desh, monsoon rains saturate the ground causing severe flooding. Europe floods from the sea may occur as a result of Atlantic storms pushing water to the coast and can be particularly damaging when occurring at high tide. Deforestation greatly increases the risk for flooding.
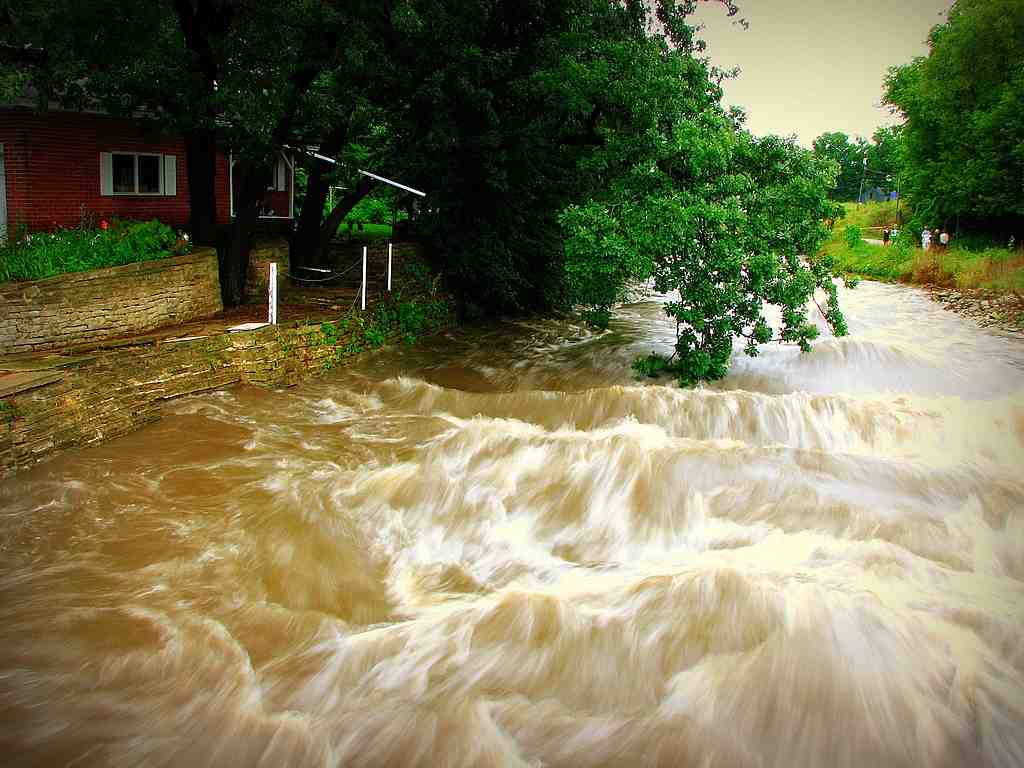

Figure 18.21 Flooding in Rochester, MN (Source: :cjohnson7 on Flickr)
Some of the worst flooding in decades also occurred during the summer of 2007. Flooding in Britain was caused by a persistent jet stream sitting further south than usual at this time of the year. System after system pounded the British Isles. During August of 2007, widespread flooding occurred in the midwest United States causing damage exceeding $115 million. A warm front advanced northward into Iowa and Illinois during mid-August where it stalled and became a stationary front. Warm, moist air overrunning the front provided the ingredients for showers and thunderstorms. Rainfall over the weekend of August 18-19, 17 inches of precipitation fell in Witoka, MN. Rochester, MN measured 6.9 inches of rainfall. The heavy rain sent streams in the region over their banks. Moisture from Tropical Storm Erin to the south enhanced the stormy conditions.
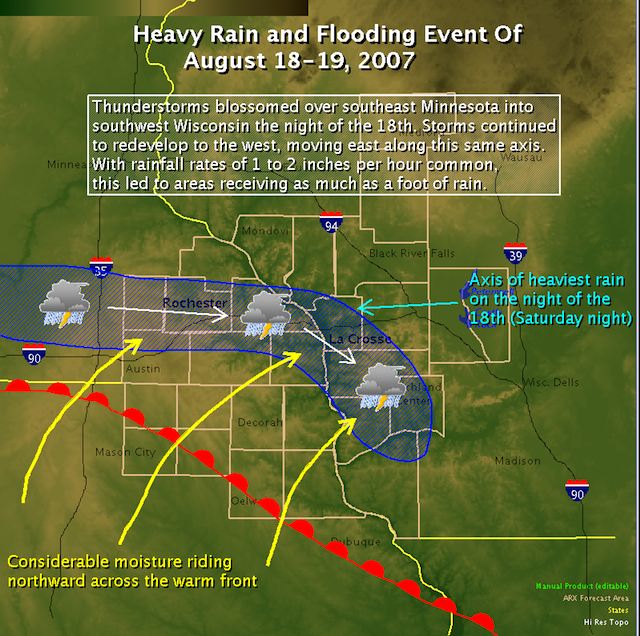
Figure 18.22 Weather Conditions during the historic rainfall and flooding event of August 18-20, 2007
Courtesy NOAA (Source)
Flood Frequency
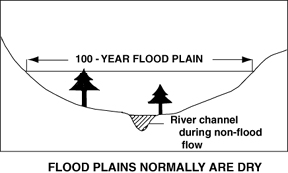 Figure 18.23 100- Year Flood Plain. Courtesy USGS
(Source
)
Figure 18.23 100- Year Flood Plain. Courtesy USGS
(Source
)
Using frequency analysis, one can estimate the probability of the
occurrence of
a given flood event The recurrence
interval, also known as the return period, is based on the
probability
that
the
given event will be equaled or exceeded in any given year. For
instance, a one
hundred year flood has a 1% chance of occurring in any given year. One
hundred
year floods are rare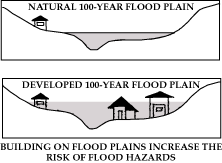 but can be devastating. The 100-year flood plain
is used
for flood plain management and insurance purposes. Those living within
this zone
are often required to have flood insurance in addition to their regular
home
owner's insurance.
but can be devastating. The 100-year flood plain
is used
for flood plain management and insurance purposes. Those living within
this zone
are often required to have flood insurance in addition to their regular
home
owner's insurance.
