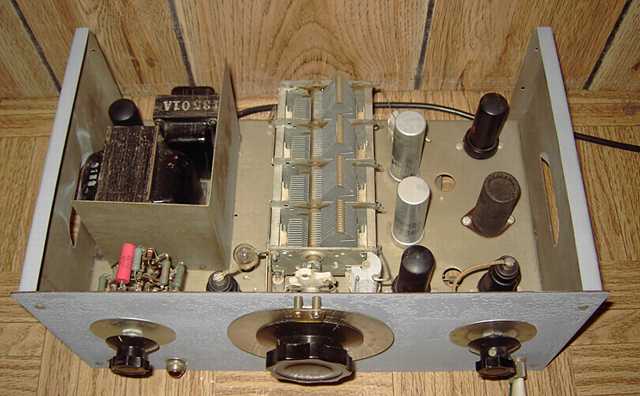
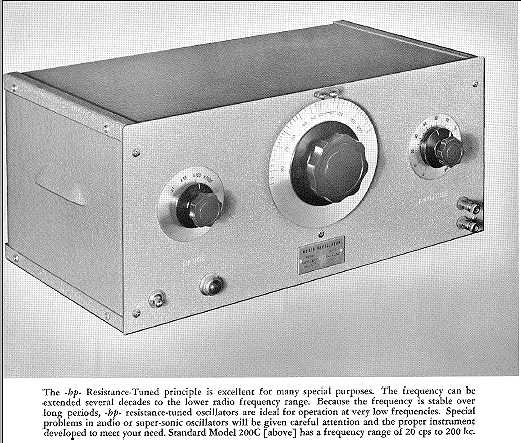
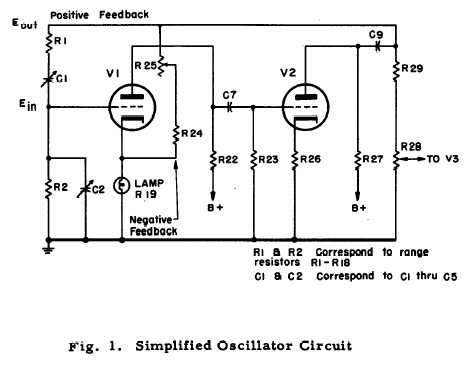
After repairing a couple of Hewlett Packard vacuum tube voltmeters, I read up on some of the company history. I was able to locate a HP-200C oscillator. This HP-200C is very close in design to the company's initial product. It is a Wien bridge resistance-tuned oscillator with the famous light-bulb stabilized negative feedback circuit designed by Wiliam Hewlett while doing graduate work at Stanford. (Patent #2268872. Application filed in 1939 and granted in 1942) The original HP-200 was built and sold out of Hewlett's garage with fellow Stanford grad David Packard, marking the founding of Hewlett-Packard.

I did not have a schematic for the 200C but the schematic for the 200I was close enough with nearly identical vacuum tubes (6F6, 6V6, and 6SJ7 for electrically identical 6J7) in the oscillator and amplifier circuits.
Output for the 200C is specified as 100 milliwatts, 10 volts into a 1000 ohm load. Although this is labeled an audio oscillator, and it does indeed cover the full audio spectrum, its upper range is well beyond audio, in the VLF radio range at 200 KHz.
Repairs
The HP-200C was in rather rough condition and had not been powered for many years. I used contact cleaner on the range switch and the volume control. The volume control had not tracked properly, but opening it and applying contact cleaner directly solved the problem. The power switch also showed no continuity. Contact cleaner was applied through the bat handle with the switch facing upwards. That cured the switch problem. The power cord was replaced with a new grounded cable. This was followed by a thorough cleaning of the set and checking for safety and a proper level of resistance in the B+ line. The rectifier was pulled out and a variac used to power the set slowly for just the filaments and checking for proper AC voltages at the rectifier socket. This was followed by a slow power-up with the rectifier in and reforming the electrolytics properly. A check with my oscilloscope showed the unit working on all its ranges. Using a frequency counter, the cap was adjusted for best dial accuracy. Apparently some of the range resistors had ben replaced earlier in its life. Dial accuracy from one range to another confirmed that the resistors were still in good order.

I noticed a low level DC bias on the output of the oscillator but learned from the 200I manual that that was normal. A 20 MFD electrolytic is used as the output capacitor. I am assuming that some leakage in the cap is the cause of the DC bias. The 200I manual warns against using the output on a high-quality audio transformer because of the DC component. The next generation HP-200CD uses special transformers for output.
Performance
The 200C proved quite stable on the scope, performing as intended. I could see the stabilizing action of the negative feedback light bulb element when switching ranges. An early HP catalog details the circuit principle and the advantages and uses for the device.
RESISTANCE TUNED PRINCIPLE
"USE THEM FOR:
ADVANTAGES
An HP-400A AC Vacuum Tube Volt Meter was the previous item on the bench.