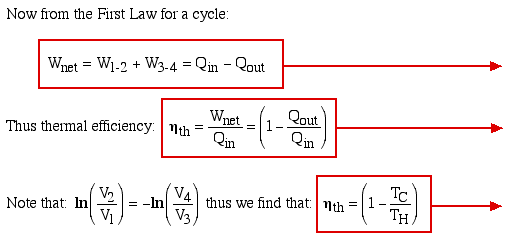Chapter 3: The First Law of Thermodynamics for
Closed Systems
b) Ideal Stirling Cycle Machines (Engines /
Coolers)
1. The Stirling Cycle Engine
Conceptually the Stirling engine is the simplest of
all heat engines. It has no valves, and includes an externally heated
space and an externally cooled space. It was invented by Robert
Stirling, and an interesting website by Bob
Sier includes a photograph of Robert
Stirling, his original patent drawing of 1816, and an animated model
of Stirling's original engine.
|
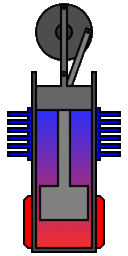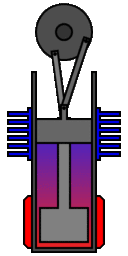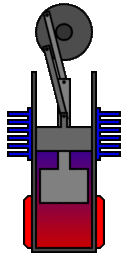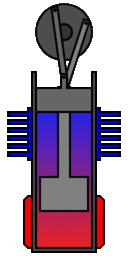
In its original single cylinder form the working
gas (typically air or helium) is sealed within its cylinders by
the piston and shuttled between the hot and cold spaces by a
displacer. The linkage driving the piston and displacer will move
them such that the gas will compress while it is mainly in the
cool compression space and expand while in the hot expansion
space. This is clearly illustrated in the adjacent animation which
was produced by Richard Wheeler (Zephyris)
of Wikipedia.
Refer also to the animation produced by Matt
Keveney in his Stirling
engine animation website. Since the
gas is at a higher temperature, and therefore pressure, during its
expansion than during its compression, more power is produced
during expansion than is reabsorbed during compression, and this
net excess power is the useful output of the engine. Note that
there are no valves or intermittent combustion, which is the major
source of noise in an internal combustion engine. The same working
gas is used over and over again, making the Stirling engine a
sealed, closed cycle system. All that is added to the system is
steady high temperature heat, and all that is removed from the
system is low temperature (waste) heat and mechanical power.
|
|
Athens, Ohio, is a hotbed of Stirling cycle machine
activity, both engines and coolers, and includes R&D and
manufacturing companies as well as internationally recognized
consultants in the area of Stirling cycle computer analysis. The
parent company of this activity is Sunpower.
It was formed by William
Beale in 1974, mainly based on his
invention of the free-piston Stirling engine which we describe below.
They developed a 1kW free-piston engine/generator, and since 1995
this technology was used by British Gas to develop CHP (Combined Heat
and Power) units – the 1kW engine/generator is currently
manufactured by Microgen
Engine Corporation (refer to their
History
and Engine
web pages).
In 2013 Sunpower was acquired by Ametek
in Pensylvania, however continues doing Stirling cycle
machine development in Athens, Ohio.
Some examples of single cylinder Stirling engines:
Stirling
Technology (note recent company name
change: Combined Energy
Technology) is a spinoff of Sunpower,
and was originally formed in order to continue the development and
manufacture of the 3.5 kW ST-5
Air engine. This large single cylinder
engine burns biomass fuel (such as sawdust pellets or rice husks) and
can function as a cogeneration unit in rural areas. It is not a
free-piston engine, and uses a bell crank mechanism to obtain the
correct displacer phasing.
Currently Combined Energy Technology
is working with Microgen
Engine Corporation, an international
company which produces the MEC 1kW free-piston engine/generator.
Combined Energy Technology has developed a multifuel burner for the
engine and is partnering with Microgen to get various systems into
the market.
Another important early Stirling engine is Lehmann's
machine on which Gustav Schmidt did the first reasonable analysis of
Stirling engines in 1871. Andy Ross of Columbus, Ohio built a small
working replica of the Lehmann
machine, as well as a model
air engine.
Solar Heat and Power Cogeneration: With
the current energy and global warming crises, there is renewed
interest in renewable energy systems, such as wind and solar energy,
and distributed heat and power cogeneration systems. Cool
Energy of Boulder, Colorado, previously
developed a complete solar
heat and power cogeneration system for
home usage incorporating Stirling engine technology for electricity
generation. This unique application included evacuated
tube solar thermal collectors (slide
courtesy of rusticresource.com),
thermal storage, hot water and space heaters, and a Stirling
engine/generator using nitrogen gas. Currently they are concentrating
on low temperature (150°C - 400°C) waste heat recovery systems
(Refer: Cool
Energy ThermoHeart 25kW Engine Overview).
Ideal Analysis: Please
note that the following analysis of
Stirling cycle engines is ideal, and is intended only as an example
of First Law Analysis
of closed systems. In the real world we cannot expect
actual machines to perform any better than 40 - 50% of the ideal
machine. The analysis of actual Stirling cycle machines is extremely
complex and requires sophisticated computer analysis (see for example
the web learning resource on: Stirling
Cycle Machine Analysis.)
The free-piston Stirling engine developed by
Sunpower, Inc is unique in that there is no mechanical connection
between the piston and the displacer, thus the correct phasing
between them occurs by use of gas pressure and spring forces.
Electrical power is removed from the engine by permanent magnets
attached to the piston driving a linear alternator. Basically the
ideal Stirling engine undergoes 4 distinct processes, each one of
which can be separately analysed, as shown in the P-V diagram
below. We consider first the work done during all four processes.
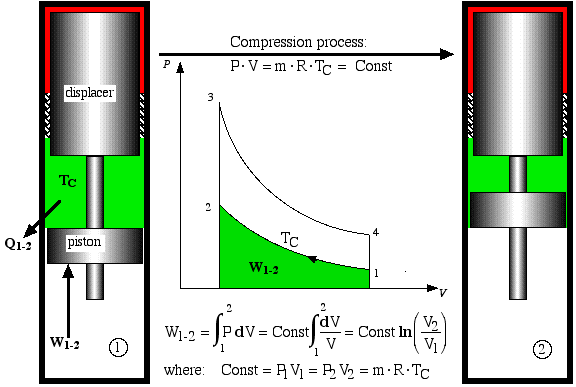
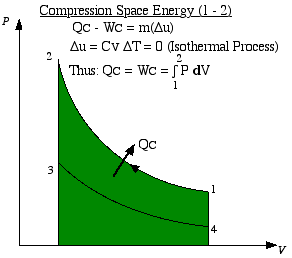
Process 1-2 is the compression process in which
the gas is compressed by the piston while the displacer is at the
top of the cylinder. Thus during this process the gas is cooled in
order to maintain a constant temperature TC.
Work W1-2 required
to compress the gas is shown as the area under the P-V
curve, and is evaluated as follows.
Process 2-3 is a
constant volume displacement process in which the gas is displaced
from the cold space to the hot expansion space. No work is done,
however as we shall see below, a significant amount of heat QR
is absorbed by the gas from the regenerator matrix.
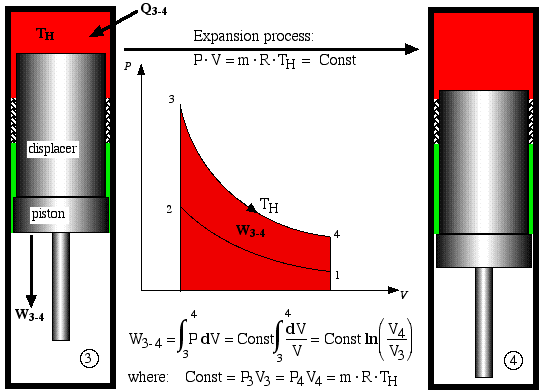
Process 3-4 is the isothermal expansion process.
Work W3-4 is done
by the system and is shown as the area under the P-V
diagram, while heat Q3-4
is added to the system from the heat source,
maintaining the gas at a constant temperature TH.
The net work Wnet
done over the cycle is given by: Wnet
= (W3-4 +
W1-2), where the
compression work W1-2 is
negative (work done on the
system).
We now consider the heat transferred during all four
processes, which will allow us to evaluate the thermal efficiency of
the ideal Stirling engine. Recall from the previous section that in
order to do a First Law analysis of an ideal gas to determine the
heat transferred we needed to develop equations to determine the
internal energy change Δu in terms of the Specific
Heat Capacities of an Ideal Gas.
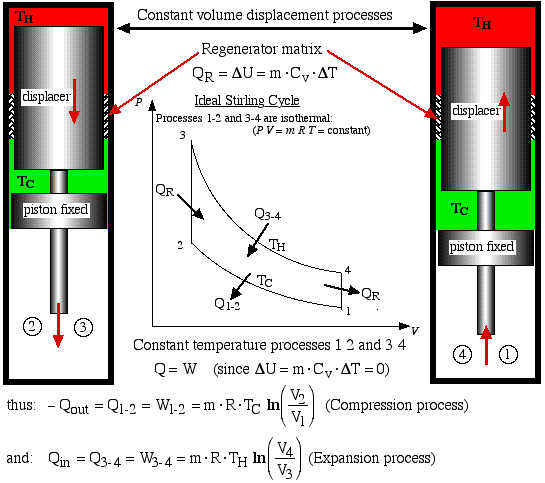
The two constant volume processes are formed by
holding the piston in a fixed position, and shuttling the gas between
the hot and cold spaces by means of the displacer. During process 4-1
the hot gas gives up its heat QR
by passing through a regenerator matrix, which is
subsequently completely recovered during the process 2-3.
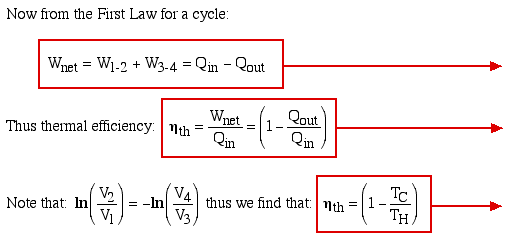
We will find in Chapter
5 that this is the maximum theoretical
efficiency that is achievable from a heat engine, and usually
referred to as the Carnot
efficiency. For more information on this subject, refer
to a paper: A
Meeting between Robert Stirling and Sadi Carnot in 1824
presented at the 2014
ISEC.
Note that if no regenerator is present the heat QR
must be supplied by the heater. Thus the efficiency will
be significantly reduced to ηth
= Wnet /
(Qin + QR).
Furthermore the cooler will then have to reject the heat that is
normally absorbed by the regenerator, thus the cooling load will be
increased to Qout +
QR. Recall that
Q2-3 = QR
= -Q4-1.
Note that the practical Stirling cycle has many losses
associated with it and does not really involve isothermal processes,
nor ideal regeneration. Furthermore since the Free-Piston Stirling
cycle machines involve sinusoidal motion, the P-V
diagram has an oval shape, rather than the sharp edges
defined in the above diagrams. Nevertheless we use the ideal Stirling
cycle to get an initial understanding and appreciation of the cycle
performance.
Problem
3.2 - The Sunpower EG-1000 Stirling
Engine/Generator
___________________________________________________________________
2. The Stirling Cycle Cooler
One important aspect of Stirling cycle machines that
we need to consider is that the cycle can be reversed - if we put net
work into the cycle then it can be used to pump heat from a low
temperature source to a high temperature sink. Sunpower
has been actively involved in the deveplopment of
Stirling cycle refrigeration systems and produces Stirling cycle
croygenic coolers for liquifying oxygen. In 1984 Sunpower developed a
free piston Duplex
Stirling Machine having only three moving
parts including one piston and two displacers, in which a gas fired
Stirling cycle engine powered a Stirling cycle cooler. Global Cooling
was established in 1995 as a spinoff of Sunpower, and
was formed mainly in order to develop free-piston Stirling cycle
coolers for home refrigerator applications. These systems, apart from
being significantly more efficient than regular vapor-compression
refrigerators, have the added advantage of being compact, portable
units using helium as the working fluid (and not the HFC refrigerants
such as R134a, having a Global Warming Potential of 1,300). More
recently Global Cooling decided to concentrate their development
efforts on systems in which there are virtually no competitive
systems - cooling between -40°C and -80°C, and they established a
new company name: Stirling
Ultracold.
Update
- 2021: Stirling
Ultracold's Ultra-Low Temperature (ULT)
freezers meets today's unprecedented COVID-19 deployment challenges.
Refer to Walgreens
COVID-19 Vaccine Case Study as well as
Stirling
Ultracold to Merge with Biolife Solutions.
We are fortunate to have obtained two original M100B
coolers from Global Cooling. The one is used as a demonstrator unit,
and is shown in operation in the following photograph. The second
unit is set up as a ME Senior
Lab project in which we evaluate the
actual performance of the machine under various specified loads and
temperatures.

A schematic diagram followed by an animated schematic
of the cooler (both courtesy of Global Cooling (currently Stirling
Ultracold) are shown below
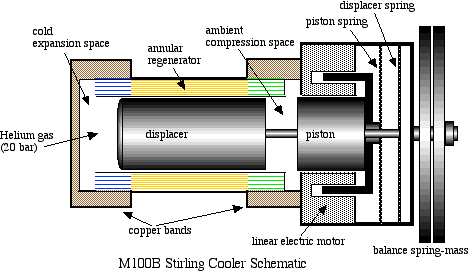
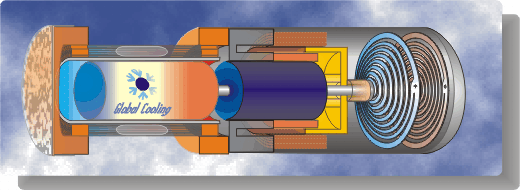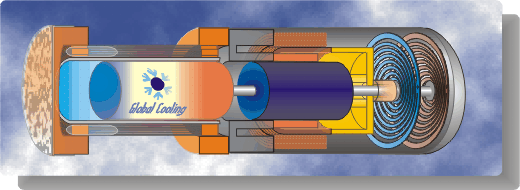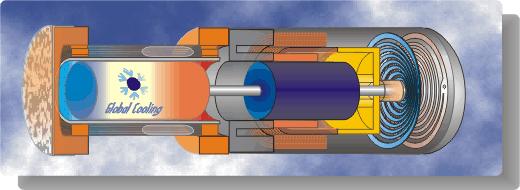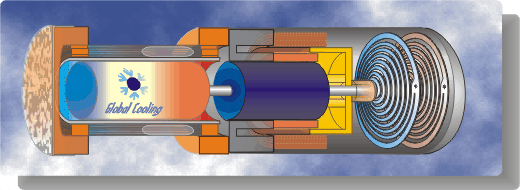
Conceptually the cooler is an extremely simple
device, consisting essentially of only two moving parts - a piston
and a displacer. The displacer shuttles the working gas (helium)
between the compression and expansion spaces. The phasing between the
piston and displacer is such that when the most of the gas is in the
ambient compression space then the piston compresses the gas while
rejecting heat to the ambient. The displacer then displaces the gas
through the regenerator to the cold expansion space, and then both
displacer and piston allow the gas to expand in this space while
absorbing heat at a low temperature.
______________________________________________________________________________________
Problem 3.3 - Stirling Cycle
Cooler M100B - Ideal Analysis
Unfortunately the analysis of actual Stirling cycle
machines is extremely complex and requires sophisticated computer
analysis. We consider the idealised model of this cooler defined in
terms of the P-V diagram
shown below in order to determine the ideal performance of the M100B
under typical operating conditions as described below. (Note
that the values presented here are not actual values of the M100B,
however were devised by your instructor for purposes of this exercise
only).
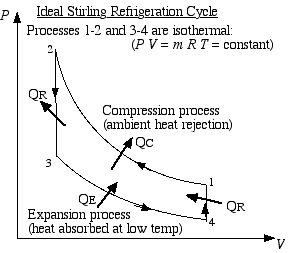
Process (1)-(2) is the isothermal compression process
at temperature TC =
30°C, during which heat QC is
rejected to the ambient. Process (2)-(3) is the constant volume
displacement process during which heat QR
is rejected to the regenerator matrix. Process (3)-(4)
is the isothermal expansion process at temperature TE
= -20°C,
during which heat QE is
absorbed from the freezer, and finally process (4)-(1) is the
constant volume displacement process during which heat QR
is absorbed from the regenerator matrix. Thus the ideal
Stirling cycle consists of four distinct processes, each one of which
can be separately analysed. State (1) is defined at a maximum volume
of 35 cm3 and a
pressure of 1.9 MPa, and State (2) is defined at a minimum volume of
30 cm3. The energy
transferred during both the compression and expansion processes is
indicated on P-V diagrams
as follows:
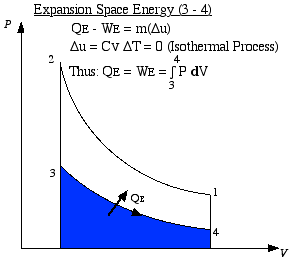
Since the working fluid is helium which is an ideal
gas, we use the ideal gas equation of state throughout. Thus P V = m
R T, where R = 2.077 kJ/kg K, and Δu = Cv ΔT, where Cv = 3.116
kJ/kg K. (refer: Ideal
Gas Properties)
a) Determine the heat absorbed in the expansion
space QE during
the expansion process (3) - (4) (Joules). Determine also the heat
power absorbed (Watts). Note that the cycle frequency is the line
frequency (f = 60 Hz). [QE
= 8.56J (power = 513.6W)]
b) Determine the net work done per cycle
(Joules): Wnet =
WE + WC
(Note that the compression work WC
is always negative). Determine also the power supplied
to the linear electric motor (Watts). [Wnet
= -1.69J (power = -101W)]
c) Evaluate the Coefficient of Performance of
the refrigerator defined as: COPR
= QE /
Wnet. (heat
absorbed in the expansion space divided by the net work done). [COPR
= 5.07]
d) Determine the amount of heat rejected by the
working fluid QR as
it passes through the regenerator matrix during process (2) - (3).
[QR
= -16.46J (power = -988
W)]
If there were no regenerator
present then this heat would need to be removed from the gas by the
expansion process in order to reduce the temperature to the cold
temperature of the freezer. How would this affect the performance of
the cooler? Discuss the importance of an effective regenerator in
the Stirling cycle cooler.
______________________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________________

Engineering Thermodynamics by Israel
Urieli is licensed under a Creative
Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.0 United States
License