Urban ClimateUrbanization has a significant impact on all elements of the atmosphere. Replacing natural vegetation with artificial surfaces alters the heat balance and hydrology of the local environment. Urban canyons affect wind speed and increased particulate content enhances precipitation down wind of a city. 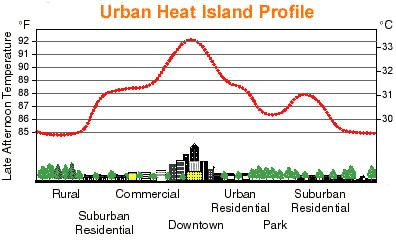 Figure 9.42 Urban Heat Island The concentration of human activities in urban areas creates an "island" of heat surrounded by a "sea" of cooler rural areas called the urban heat island. Heat is added to the urban atmosphere by industry, transportation, exhaust heat, and air conditioning among other things. Artificial surfaces with low albedo absorb much insolation, heating the surface more than if it were a natural surface like grass. The additional heat can create differences in air temperature between the city and countryside of 10o C (18o F) or more. Consequently, snow disappears earlier and vegetation bloom earlier in the city. Sunlight is trapped within the "urban canyon" by reflective surfaces. Building materials like brick and asphalt have high heat conductivity. Heat loss in the evening can compensate for that which has been gained during the day.
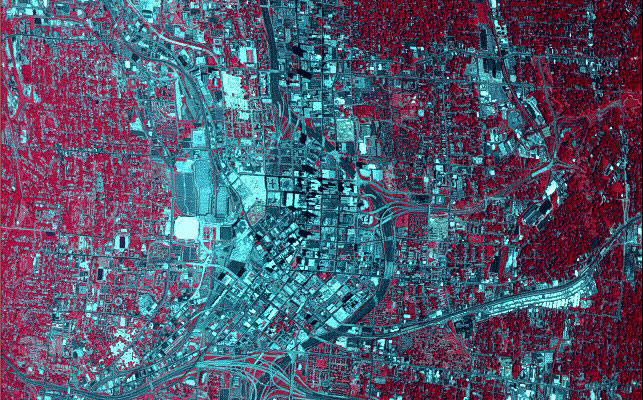
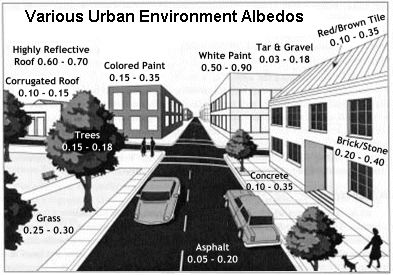
Figure 9.43 Typical albedos. The warm city surface induces convection that draws urban air upwards, which is then replaced by cool air from the countryside. This rural-urban circulation is more likely to occur when synoptic-scale winds are light. The rising air transports dust and other particulates upward, gathering as a dust dome. If synoptic-scale winds are strong enough, the pollutants spill over the city boundary and stretch downwind over the countryside as a pollution plume. Particulates concentrated in the urban atmosphere serve as nuclei for the condensation of water. Several studies have shown how precipitation is enhanced downwind of an urban area due to increased particulate content from urban sources. Click play button to view Figure 9.44 Urban heat island and air circulation. In rural areas, more available water for evaporation keeps surface temperatures cooler. Impermeable artificial surfaces in the city increase water runoff and reduce infiltration. This results in less moisture available for evaporative cooling and higher sensible transfer than in the surrounding rural areas.
Figure 9.45 Atlanta, GA. urban heat island.
|