The OceansIt's obvious why Earth is called the "Blue Planet" as 71 percent of the surface is covered by water, 97% of which is in oceans. Oceans appeared on Earth between 3 and 4 billion years ago from which sprang life. Ancient algal formations found in the water near Australia called stromatolites are thought to have been the early source for oxygen in the atmosphere. Oceans & SeasFive principal oceans the Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Southern and Arctic comprise the "world ocean" that surround the Earth's continental land masses. The Pacific Ocean is the largest covering 166 million square kilometers (64 million square miles) of the surface with an average depth of 4200 meters (14,000 ft). At nearly half the size, the Atlantic Ocean occupies 83 million square kilometers (32 million square miles) with an average depth of 3900 meters (13,000 ft). With a similar average depth, the Indian Ocean is slightly smaller at approximately 73 million square kilometers (28 million square miles). The Southern Ocean surrounds Antarctica and was recognized in 2000 as an ocean by the International Hydrographic Organization. It encompasses roughly 20.3 million square kilometers (7.8 million square miles) with a typical depth between 4,000 and 5,000 meters (13,000 to 16,000 feet). The Arctic Ocean is the smallest covering 13 million square kilometers (5 million square miles) with an average depth of 930 meters (3250 ft). Some view the Arctic Ocean as a sea rather than ocean because of its small size.
Figure 2.17 World's Oceans
Seas are salt-water bodies smaller than oceans and partially enclosed by land. Major seas include the Mediterranean, Baltic, Bering, Black, Caribbean, Coral, North, Red, and Yellow. Unlike inland lakes that can be salt or fresh water, there is a constant exchange of water between ocean and sea. Several inland salt lakes like the Aral, Caspian, and Dead are erroneously named "seas". The Nature of Ocean WaterSea water makes up the largest store of water in the
hydrologic cycle. It is comprised of nearly 60 chemical substances with
common salt being the most abundant, 78% of the dissolved solids. Ocean
salinity varies from 32 - 37 parts per thousand. Salinity is lower near
land and in the polar regions (30 ppt). A number of factors determine ocean salinity. Salinity is lower where freshwater rivers enter the ocean. In the North Pacific precipitation exceeds evaporation thus diluting ocean water. Water is more saline in subtropical oceans where evaporation exceeds precipitation. The Atlantic ocean is the most salty while the Arctic ocean is the least. The oceans exhibit three vertical temperature zones, 1) a surface layer of water, 2) a transition zone of decreasing temperatures with depth, and 3) the cold waters of the deep ocean. The zone of transition, known as the thermocline, is most noticeable where surface water is warmest. Polar water may have no thermocline as the surface temperature are very cold.
|
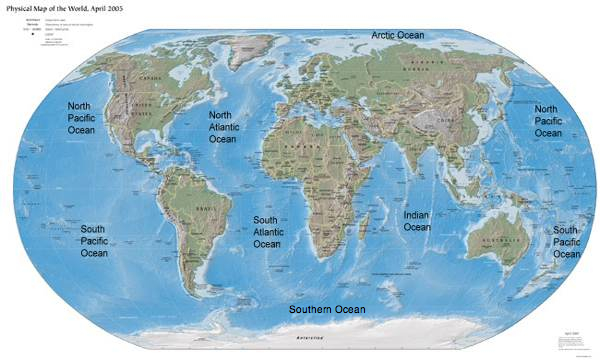
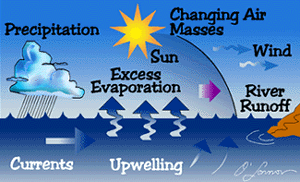 Figure 2.18 Controls over ocean salinity. (Courtesy
Figure 2.18 Controls over ocean salinity. (Courtesy 