The SunThe Sun is a giant thermonuclear furnace with an
internal temperature estimated to be 15 million degrees Celsius.
Hydrogen nuclei collide at such an extremely high speed they fuse to
form helium nuclei generating enormous amounts of heat in the Figure 2.3 Structure of the Sun
Watch: "Where does the Sun get it's energy?"
|
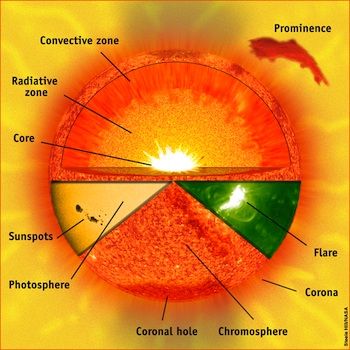 core. The
heat works its way to the luminous outer surface called the photosphere.
Here temperatures fall to about 6000oC
generating a maximum wavelength of emission in the visible end of the
electromagnetic spectrum. Above the photosphere lies the chromosphere and the corona. The chromosphere acts as
a boundary between the cooler photosphere and hotter outermost layer
the corona.
core. The
heat works its way to the luminous outer surface called the photosphere.
Here temperatures fall to about 6000oC
generating a maximum wavelength of emission in the visible end of the
electromagnetic spectrum. Above the photosphere lies the chromosphere and the corona. The chromosphere acts as
a boundary between the cooler photosphere and hotter outermost layer
the corona. 