Map projections
A map projection is a method of portraying the curved surface of the Earth on a flat planar surface of a map. Projections are created to preserve one or several measurements of the following qualities:
Each projection handles the conversion of these metric properties from the
curved surface of a globe to the flat surface of map differently.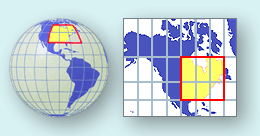
Figure 1.19 Visualizing a map projection (Courtesy USGS. Source)
The purpose of the map is of primary importance in choosing a projection to illustrate spatial patterns of Earth phenomena. For instance, the Mercator projection was long used for navigation or maps of equatorial regions. The cylindrical Mercator projection mathematically projects the globe onto a cylinder tangent to the Equator. Large areas become distorted which increases toward away from the Equator. Distances are true only along the Equator, special scales are provided for other latitudes for measurement.

Figure 1.20 Cylindrical Mercator projection
(Courtesy USGS
- Source)
The Robinson projection uses tabular coordinates rather than mathematical formulas to make earth features look the "right" size and shape. A better balance of size and shape result is a more accurate picture of high-latitude lands like Russia, Soviet and Canada. Greenland is truer to size but compressed.
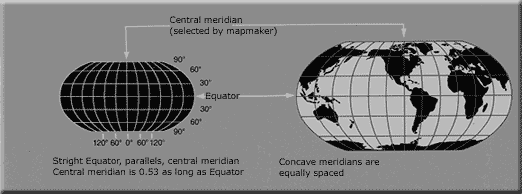
Figure 1.21 Robinson projection
(Courtesy USGS
- Source)
For more on projections see: Map Projections from the United States Geological Survey.
