Chapter Review
|
Shield Volcano |

Composite Volcano |
Cinder Cone |

Mt. Saint Helens, Courtesy USGS
 Click image to enlarge |
 Click image to enlarge |
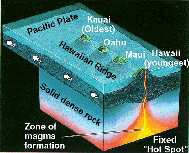
Hawaiian islands forming Source: USGS |
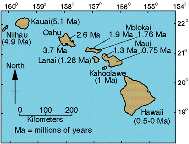
Age of Hawaiian Islands Source: USGS |


