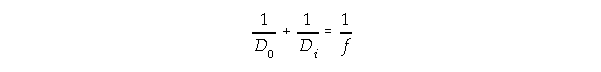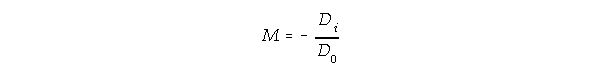Mirrors Mirrors
To find the image in a particular mirror of a point on an object, we
must find out what happens to the light rays from this object point that
strike the mirror. This procedure is complicated because the law
of reflection has to be applied to each of those rays.
The process of
 Ray Tracing Ray Tracing
uses these rays to find the image.
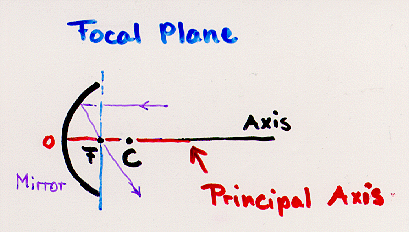
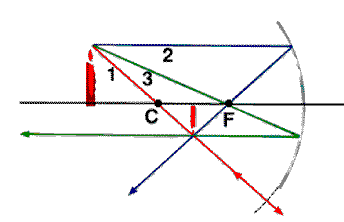
F : Focal Point
Focal Length f: Distance of the surface of the mirror O to the
foval point F.
The reflecting surface of a concave mirror bows away
from the light source like a cavity. This means that the
center C of the sphere forming the mirror is in front of the mirror.
The focal length f is positive for concave mirrors.
The images in a concave mirror can be found by
ray tracing.
 Ray Rules Ray Rules
- All rays that (when extended) pass through C are
reflected back on themselves.
- All rays that (when extended) pass through F are
reflected back parallel to the axis.
- All rays incident parallel to the axis are reflected
so that they appear to be coming from the focal point F.
- Parallel ray rule: Rays parallel to each other are
imaged on the focal plane
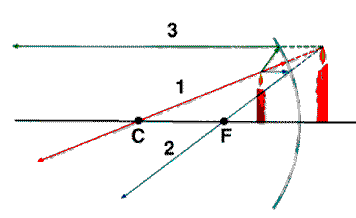
Concave mirrors can be found in flashlights.
Concave mirros can produce real images as
well as virtual images.
A convex mirror is a mirror that bulges toward the
light source.
Light rays are illustrating
the ray rules for rays incident on a convex spherical mirror.
Ray tracing shows that the image in a convex mirror is
a virtual image: no light actually comes from it. It is
also erect and closer
to the mirror and smaller
than the object.
Look at a spoon!
Tutorials:
Reflection in a concave mirror - Ray diagrams
Reflection in a convex mirror - Ray diagrams
 Equation for
Spherical Mirrors: Equation for
Spherical Mirrors:
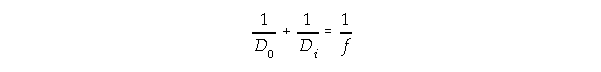
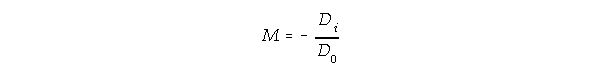
with
| f
| :
| focal length --> f = R/2
|
| R
| :
| radius of mirror
|
| D0
| :
| distance of object
|
| Di
| :
| distance of image
|
| M
| :
| magnification
|
The magnification of a mirror is given by
M = -Di / Do
and determines the image characteristics
Tutorials:
Mirror equation for a concave mirror
Mirror equation for a convex mirror
 Mirrors in Art Mirrors in Art
M.C. Escher: Stilleben mit spiegelnder
Kugel, 1934
M.C. Escher: Die Pfuetze, 1952
 Anamorphic Art Anamorphic Art
A
cylindrical anamorph needs
a cylindrical mirror to be reconstructed.
23 Amazing Anamorphic
Artwork that need a mirror cylinder to reveal their beauty.
| 

 Mirrors
Mirrors  Magnification
Magnification Magnification
Magnification Mirrors in Art
Mirrors in Art  Mirrors in Art
Mirrors in Art  Anamorphic Art
Anamorphic Art  Anamorphic Art
Anamorphic Art 
 Ray Tracing
Ray Tracing