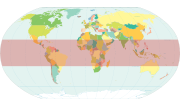
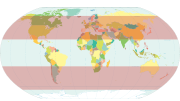
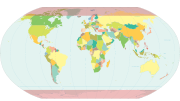
Geographical ZonesNatural systems of climate, vegetation, and soil change substantially as one travels from the equator to the pole due largely to the latitudinal variation in energy input to the earth system. The early Greek scholar Aristotle was the first to divide the Earth into zones based on climate. His "torrid zone", thought to be too hot for human habitation, lay between 23.5o N and 23.5o S. Aristotle thought that the "temperate zones" between 23.5o N - 66.5o N and 23.5o S - 66.5o S were the only livable zones. From the arctic (66.5 N) and and antarctic circles (66.5 S) to the the poles (90 N and S) were the uninhabitable "frigid zones".
Geographers continue to use
latitudinal variation of climate
characteristics as a way of dividing the Earth into fairly
homogeneous geographical zones. These zones are: [Figure 1.39 Geographical Zones Not Available Yet] The equatorial zone is characterized by warm temperatures and nearly uniform day length throughout the year. The boundary of the tropical zone lies close to the Tropic of Cancer (23.5oN) and Capricorn (23.5oS), the latitudinal limit where the Sun is directly over head at noon at different times of the year. The subtropical zone includes Aristotle's home of Greece, and seasonal changes in temperature become more pronounced. The temperate midlatitude zone is noted for is variable weather conditions. Large annual swings in temperature are characteristic of the subarctic and subantarctic zone where extensive areas of cold air form during winter and milder conditions prevail during summer. The coldest zones are the Arctic and Antarctic, where the Sun never rises above the horizon for several months at a time. Much of the light that does reach the surface is reflected off the light colored surfaces of the North (sea ice) and South (mostly glacial ice) poles. The coldest zones are the North and South Polar. Like the Arctic and Antarctic Zones, the Sun never rises above the horizon for many months of the year. The coldest temperatures are near the South Pole, far from any moderating influence of an ocean and the little light that does make it to the surface is reflected from glacier ice.
|
|||
|
Contents |Glossary | Atlas | Index | Blog | Podcast | Google Earth | Search | Updates | Top of page About TPE | Who's Used TPE | Earth Online Media Please contact the author for inquiries, permissions, corrections or other feedback. For Citation: Ritter, Michael E.
The Physical Environment: an Introduction to Physical Geography.
Michael Ritter (tpeauthor@mac.com) |
|||
|
Help keep this site available by donating through PayPal. |